WHAT MAKES A MEDICAL EMERGENCY?
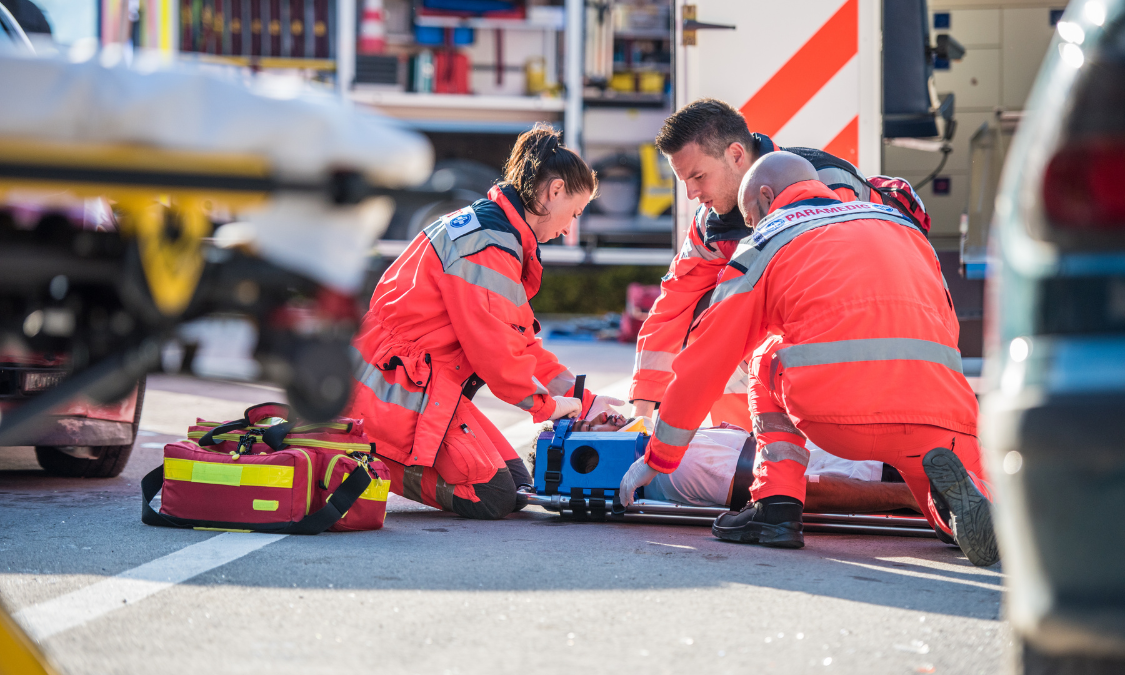
The term medical emergency can mean many things depending upon the context in which it is used. There are a variety of scenarios all of which befit the term emergency. The term emergency can mean very different things when used in an ICU compared to when it's used in an ambulance, namely the severity, treatment needed and the steps to manage the emergencies may be very different.
Let us consider the example of a patient who has had an airway collapse, in an ICU or hospital setting this is an emergency, but one that can be handled quite easily with either intubation or by doing a cricothyroidotomy to establish an airway. Now consider the same patient with the same problem, only this time he is in an ambulance and he is being transported to the hospital, in this situation where the patient is surrounded by only paramedics, in this case, the emergency is more urgent and the chances for the patient to die is higher.
Hospital-based care can quickly triage and treat various patients and emergencies mainly because:
- They have the necessary advanced scanning and diagnostic equipment available.
- Safety and zero chance of infections
- Multiple specialists and doctors work together to treat the patient.
- Availability of sterile surgical fields and equipment.
- Availability of various medications and materials.
WHAT IS THE ROLE OF TELEMEDICINE?
Telemedicine is basically a subset of medicine wherein the doctor and patient are not located at the same physical location but are separated by time and distance. The main idea behind the deployment of telemedicine was to provide access to healthcare to remote communities that had traditionally lacked it. It was always an unstated understanding that the patients would be referred to or seen at a hospital in the case of true life-threatening emergencies.
However as can be seen even today in the remote regions of countries such as India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, etc, even routine medical conditions can become emergencies by the time the patient makes it to the nearest hospital. A simple case of malaria, chicken pox, appendicitis, etc can develop into fatal complications before adequate care and medications are given to the patient. Recently Telemedicine has been focusing on providing triage, medications and instructions to the locally situated healthcare worker, all this is to manage emergent conditions and to prevent the patient from worsening.
India and other countries have established certain protocols for doctors to triage patients over a telemedicine consult and prescribe medications. This means that the ways in which telemedicine can be used have drastically improved, with rapid advancements in both mobile-based applications, devices and technology Telemedicine is currently on steroids! Both public and private players are now swarming onto the telemedicine scene. Today, telemedicine is now being deployed even in the sphere of EMS Services
WHAT CONSTITUTES A TELE-EMERGENCY?
In scenarios where telemedicine is being used from tertiary care centres, remote hospitals, rural centres, etc, the most common emergencies include:
- Trauma
- Pregnancies and complications
- Infectious diseases
- Pandemics/endemics
- Neonatal emergencies
- Snake bites
Another place where both private and govt. players are now deploying telemedicine solutions in speciality care. This means that there are telemedicine service providers who provide targeted services for specific medical specialities such as Psychiatry, Neurology, Pain Management, Nephrology, etc. In such cases, the emergency would depend on the speciality involved.
Some case scenarios for example are,
- A suicidal patient, a woman who has gone through sexual abuse, a schizophrenic patient etc are emergencies in terms of psychiatry.
- A sudden abdominal pain indicative of appendicitis in a child located in a remote village is an emergency for pediatric care.
- Reddish-brown urine, and blood in stools in a chronic alcoholic can be an emergency for nephrology.
- A sailor on a ship who is suffering from malaria or tropical fever becomes an emergency because of the distance from medical care.
- A windpipe obstruction on an aeroplane becomes an emergency due to the terrain and scenario.
TERRAIN BASED CARE
Normal medical conditions can worsen and become a medical emergency based on the terrain. Just consider that the massive increase in the funding for and research in telemedicine was spurred on by the space race. With countries competing to see who could put more people, for a longer time in space, suddenly the health of astronauts floating thousands of miles above our heads ( far out of reach of phones and the internet ) became a priority. Even today all ships whether they are sailboats, fishing vessels, military vessels, cruise liners or cargo ships, face medical issues that can quickly spiral into emergencies. Many a first-time flier has had a panic attack on board a flight and it has quickly escalated into a life-threatening emergency, mass panic on board, thus necessitating a return to the airport.
In the case of remotely located regions, such as the arctic or antarctic, where scientists and researchers often bunker down for months at a time, something as simple as a scratch by a rusty nail can become fatal since they are located so far away from sophisticated medical help. So when these places are connected by telemedicine, there is a separate checklist and triage protocol which is followed.
IN EMS SERVICES
The latest area in which Telemedicine is being deployed to great use is in the sphere of emergency medical services. Telemedicine in emergency care services can transform ambulance crews from providing reactive care to proactive care. Decisions, diagnoses and treatment modalities unknown to the paramedics can be supplemented by a doctor via Teleconsultation. In EMS services there are many emergencies that can be tackled with the additional help of a doctor on a teleconsult. Many mobile-based and web apps have created built-in workflows specifically for paramedics, to be deployed in the field. This includes the use of Bluetooth-enabled peripheral devices, that can record vitals and other health data, and port them in real-time to any remotely located doctor or hospital.
What Are The Advantages?
In many accidents, the golden hour and initial treatment window are the most vital for the survival of the patient with the least number of complications. When we start a telemedicine consult at the same time as the patient is being picked up, a doctor or even multiple specialists can help the paramedics in making decisions regarding what should be the care given to the patient. There are medical emergencies such as cardiac episodes, strokes, pregnancies, miscarriages, psychiatric episodes, etc, all of which require specialised care and it can be hard for a paramedic or rookie doctor on the scene to connect with one. Ambulance drives can be anywhere from a few minutes, to an hour. During this time effective treatment can be initiated and most importantly the nature of the emergency can be addressed. By the time the ambulance arrives at the hospital, staff and the required specialists can be alerted and be waiting to receive the patient.
All of this massively reduces the mortality and morbidity of the patient and leads to better long-term outcomes and a faster recovery for the patients. After all the principal objective of healthcare is not just to treat diseases, but also to improve the quality of life.
TAKEAWAYS
Medical emergencies can be of many types and of varying severities based on the situation/scenario. The use of Telemedicine can greatly enhance emergency care in any situation. The use of Telemedicine is only limited by our imagination and technology, as such, it can be deployed on land, at sea, or in the air. The addition or use of Telemedicine can drastically improve treatment outcomes for patients, helps avoid preventable deaths and improves the overall timeline and quality of medical care.
Unlike conventional medical care, Telemedicine can be far more versatile and flexible in its applications across various terrains and in myriad scenarios. This can be invaluable in providing equitable access to healthcare in remote areas, rural communities, developing countries with large populations, poor countries with poor infrastructure and resource allocation, marginalized communities and LGBTQ communities across the world.