What Is A Remote Health Monitoring System?
It is more important than ever to develop new approaches to remote patient care in light of the COVID-19 pandemic's social isolation norms. It is understandable why major internet companies like Microsoft and Amazon are investing heavily in digital healthcare, with a particular focus on Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM).
Innovation in RPM is good news for patients diagnosed with chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes as well. Damage from these diseases accelerates fatalities.
Enhanced monitoring with the help of Artificial Intelligence-aided analytics could help diagnosticians control the extent of this damage with timely medical intervention. Additionally, cloud computing technologies and the right Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems help create a robust RPM network.
Reducing the Risk of Contagion with RPM
Long before even COVID-19, the probability of spreading viruses and hospital-acquired infections was observed to increase with the duration of a patient's hospital stay.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data points out that hospital stays accounted for a 17.6% risk of patient infection with a 1.6% daily increase.
Therefore, the need for secure healthcare delivery with telemedicine software is more crucial than ever before.
Most hospitals continue to rely on manual spot-checks for monitoring a patient's condition every 4-6 hours, which makes matters worse. There are extended periods when deterioration in a patient's condition tends to go unnoticed.
Healthcare professionals are not receiving the most updated patient info at all times. Things get even more complicated when the nursing staff's shift timings change.
How RPM Helps Medical Experts
The widespread adoption of RPM with AI-powered real-time data analytics is necessary to address all of the aforementioned problems. Medical professionals can prioritise care effectively and make intelligent judgments with RPM data.
This ability to prioritise is necessary in order to effectively triage patients and treat the most serious ailments first when the ward becomes overcrowded. Data from RPM devices like oximeters, spirometers, and apnea monitors are organised into understandable levels using AI-powered analytics. Then, hospital resources and the advice of the appropriate medical professional can be used. Thousands of patients can have their data analytics performed simultaneously and in real-time.
The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) determined that with AI-powered RPM, the future of medicine will be able to:
- Cut down patient readmissions by 38%
- Reduce emergency room calls by 25%
- Boost patient satisfaction by 25%
- Cut overhead by more than 17%, and
- Improve Medicaid compliance by 13%
Major Elements of RPM
An RPM can be segmented in the same way you would segment the various modules of an Internet of Things (IoT) setup. The high-level components of RPM can then be defined as the following:
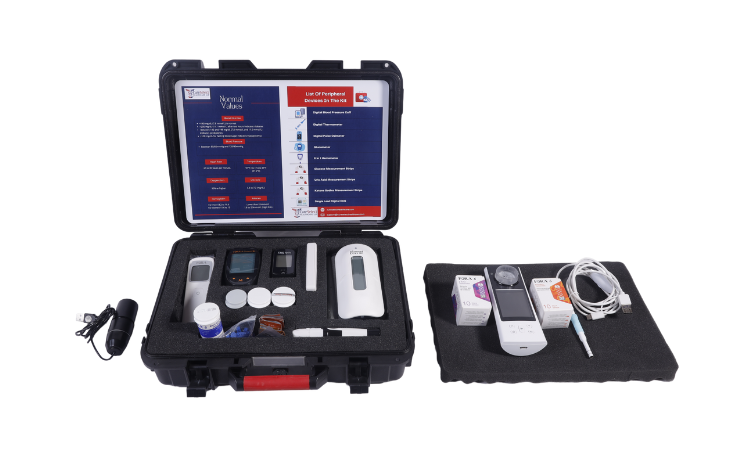
- Personal Monitoring Device
These gadgets often have a Bluetooth module and record all the necessary patient data. All kinds of health factors, such as blood pressure and heart rate, are tracked via sensors implanted under or over the skin or by wearable technology.
For the time being, only non-invasive devices that measure a fundamental set of physiological events would be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). All wearable technology must be capable of sending patient measurements to the medical professional. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communication is the method that is most frequently used for this transfer.
- Patient-side mobile application
The clinician receives patient data from the wearables via a smartphone app. These apps need to be BLE data exchange network compliant and have caching features to protect against connectivity problems.
The application should be integrated with the healthcare provider's system via a secure API built on Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards. In order to make the programme enjoyable for patients to use, it is typically created with instructive images and top-notch UX design. These apps offer access to educational information, video calling capabilities, and medicine reminders.
The wearable device of the patient can send raw data to a cloud repository. This data is sorted into manageable, tagged clusters using analytics powered by AI. For RPM devices, a number of systems provide direct-to-cloud connectivity, wherein all the recorded data is stored in the cloud.
- Hospital Side Web Application
Similar to the patient-side app, a hospital-side web app adheres to Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations. To communicate with the hospital administration's Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system, it makes use of FHIR-capable APIs. Additionally, this app has a one-on-one connection with the departmental data silos.
Other modules
Additionally, some or all of the modules listed below are part of the RPM setup:
- Decision support: Before delivering the patient's vital signs to the doctor, this module copies them from the repository and compares them to the expected values.
- Reporting: The RPM system generates reports for the medical personnel using all pertinent patient metrics and manual inputs.
- Notification: A warning message is issued to the appropriate doctor or consultant if the decision support module detects irregularities in the patient data.
- Analytics: Real-time conclusions are drawn from the patient data using Business Intelligence (BI) and AI-enabled data visualisation tools. These inferences can be used by doctors to forecast hazards and make informed treatment choices.
Popular RPM Devices and Upcoming Prototypes
By the end of 2022, more than 4 million patients would be monitored remotely worldwide, according to an IHS Markit survey from 2020. The use of RPM will rise by 34% in the coming year alone, thanks to Big Tech's continual developments. The following are some products that are sweeping the medical device market:
- Microsampling Devices
Devices for collecting samples remotely are becoming more and more common, particularly those that use the Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling (VAMS) method. Blood from the fingertip is sufficient thanks to current analytics tools because its volumetric variance is less than 5%. VAMS does away with the requirement for traditional phlebotomy and venous blood collection.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors
These devices can track blood sugar levels throughout the day and identify high levels using a sensor implanted under the skin. While doctors can remotely use these devices, parents of children with Type-I Diabetes can also monitor their readings and respond quickly when they reach dangerous levels.
- Inexpensive Surgical Automation
The surgeon's inability to precisely access some locations inside the human body is overcome by these tools. Although investing in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for surgical tools is expensive, a number of businesses, including Riverfield and Stryker, are working on ways to mass-produce these tools at competitive pricing.
These instruments would give surgeons enlarged projections of the intended organ and cutting-edge technology to safely access them.
- AI-enabled Vision
By the end of 2021, AI will improve computer vision, making it possible to use it to obtain visual features of patient vitals more quickly. The estimation of blood loss or haemorrhaging in mothers during or after childbirth will be the first use of this technology.
This device will be especially important in remote and hard-to-reach locations where gynaecological intervention is scarce.
Conclusion
RPM systems assist individuals in taking a more active role in their own health management in addition to assisting doctors in treating a significantly bigger volume of patients. When unforeseen accessibility challenges are anticipated to arise in the upcoming years, these technologies will continue to gain in importance. Additionally, doctors would be able to use RPMs' cloud computing and AI-enabled data analytics for better diagnostic and treatment precision. You can consult our telemedicine solutions for the development of custom healthcare software to learn more about the enormous potential of RPM to optimise your delivery of healthcare.