The Silver Tsunami: India's Rising Elderly Population and the Healthcare Dilemma
India, like many other countries, is witnessing a significant demographic shift characterized by a rapidly growing elderly population. Advances in healthcare, improved living standards, and declining birth rates have contributed to increased life expectancy, leading to a burgeoning cohort of seniors. While longevity is undoubtedly a cause for celebration, it also presents unique challenges, particularly in the realm of healthcare. The existing healthcare infrastructure in India is ill-equipped to meet the evolving needs of this demographic, highlighting the urgent need for innovative solutions. In this article, we explore the rising elderly population in India, the unpreparedness of the healthcare system, and the role of technology, such as telemedicine, in improving their quality of life.
The Silver Surge: A Demographic Reality
India is experiencing a demographic transformation characterized by a growing proportion of elderly individuals. According to the United Nations Population Division, the number of people aged 60 and above in India is projected to reach 319 million by 2050, comprising nearly 20% of the total population. This demographic shift is attributed to various factors, including advancements in healthcare, better sanitation, and changing lifestyles. While longer life expectancy is a testament to improved healthcare outcomes, it also presents unprecedented challenges for the healthcare system.
Healthcare Unpreparedness: A Looming Crisis
Despite the rising numbers, India's healthcare infrastructure is woefully unprepared to address the unique needs of the elderly population. The existing healthcare system is primarily designed to cater to acute and infectious diseases, with limited focus on chronic conditions and age-related ailments. Accessibility to specialized geriatric care facilities, trained healthcare professionals, and affordable medication remains a significant challenge, particularly in rural areas. Additionally, the socio-economic disparities exacerbate the healthcare gap, with marginalized elderly populations facing disproportionate barriers to access and affordability.
The Role of Technology: Telemedicine as a Game Changer
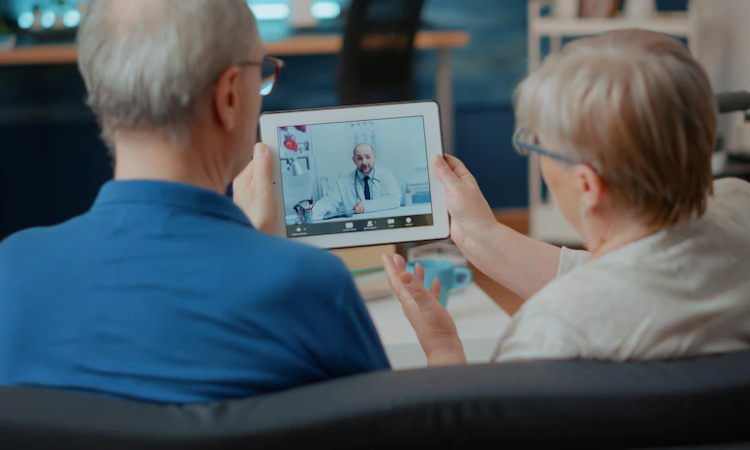
In the face of these challenges, technology emerges as a potent tool for revolutionizing healthcare delivery for the elderly population in India. Telemedicine, in particular, holds immense promise in bridging the gap between patients and healthcare providers, especially in remote and underserved areas. Through telemedicine platforms, elderly individuals can access healthcare services remotely, thereby overcoming geographical barriers and minimizing the need for physical mobility. Virtual consultations enable seniors to receive medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations from qualified professionals without the inconvenience of travel or long wait times.
Benefits of Telemedicine for Elderly Care
Telemedicine offers a plethora of benefits that are particularly relevant to the elderly population:
- Accessibility: Telemedicine enhances access to healthcare services for seniors living in rural or isolated areas, where healthcare facilities are scarce.
- Convenience: Virtual consultations allow elderly individuals to seek medical advice from the comfort of their homes, reducing the physical and logistical challenges associated with in-person visits.
- Timely Intervention: Telemedicine enables early detection and management of health issues, thereby preventing complications and improving overall health outcomes.
- Continuity of Care: Seniors with chronic conditions can benefit from regular monitoring and follow-up consultations through telemedicine, ensuring continuity of care and adherence to treatment plans.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Telemedicine eliminates the need for travel expenses and reduces healthcare costs associated with frequent hospital visits, making healthcare more affordable and accessible for elderly patients.
Challenges and Opportunities
While telemedicine holds immense potential, its widespread adoption in India faces several challenges, including technological barriers, regulatory constraints, and digital literacy issues among the elderly population. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from policymakers, healthcare providers, technology developers, and community stakeholders. Investments in digital infrastructure, training programs for healthcare professionals, and targeted initiatives to enhance digital literacy among seniors are essential steps toward realizing the full potential of telemedicine in elderly care.
Conclusion: Toward a Future of Age-Inclusive Healthcare
The rising elderly population in India presents both a demographic dividend and a healthcare dilemma. To ensure a future of age-inclusive healthcare, it is imperative to adapt and innovate in response to the evolving needs of seniors. Technology, particularly telemedicine, emerges as a transformative force in addressing the healthcare challenges faced by the elderly population. By leveraging the power of telemedicine to provide accessible, affordable, and quality healthcare services, India can pave the way for a future where seniors can age gracefully with dignity and well-being.