Unlocking Telemedicine Integration: Best Practices and Pitfalls to Avoid
Introduction:
As telemedicine continues to revolutionize healthcare delivery, the integration of third-party telemedicine applications with hospital electronic medical records (EMR) and billing systems has become increasingly common. This integration offers numerous benefits, including improved patient care coordination, streamlined workflows, and enhanced efficiency. However, it also presents challenges and potential risks that healthcare organizations must carefully consider.
There are many new software companies coming up that are part of a wave that can be called software as an export rather than the traditional SaaS (software as a service). As the digitization of the world is expanding, more and more countries are opting to digitize their healthcare systems for convenience and ease of access.
Having a centralized system saves time and effort, avoids the need for duplicates and tedious paper records and most of these companies provide value-added services such as automated billing or pushing the patient encounters to systems such as ECW or Epic.
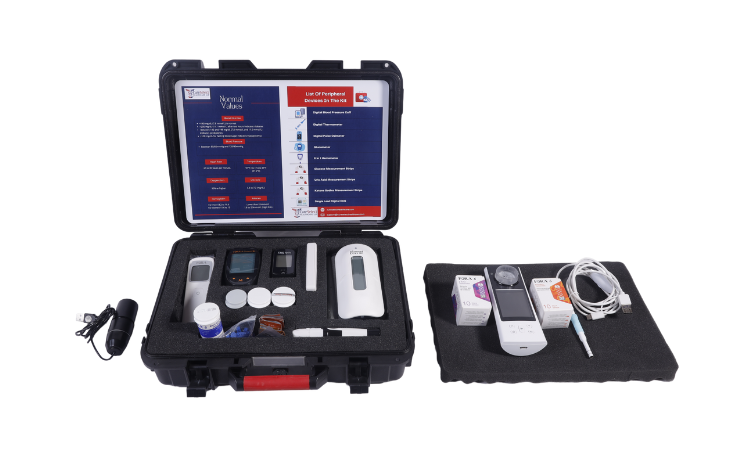
For telemedicine software that is presented by third parties, a direct link to the hospital EMR and records can be a necessity as otherwise the application cannot access the patient database and any consults or treatments have to be manually entered again by hospital staff.
In this article, we explore whether third-party telemedicine applications can be safely linked with hospital EMR and billing systems, the requirements for third-party companies, the associated risks, and federal regulations governing this practice.
Opportunities:
Integrating third-party telemedicine applications with hospital EMR and billing systems can provide several advantages for healthcare organizations, providers, and patients:
- Enhanced Care Coordination: Seamless integration allows for the exchange of patient data between telemedicine platforms and hospital EMRs, enabling better care coordination and continuity across different care settings
- Improved Efficiency: Automation of administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling, documentation, and billing, can streamline workflows and reduce administrative burdens for healthcare providers.
- Expanded Access to Care: Telemedicine integration can extend the reach of healthcare services to remote or underserved populations, improving access to care and reducing disparities in healthcare delivery.
- Patient Convenience: Patients benefit from the convenience of accessing healthcare services remotely through user-friendly telemedicine platforms, eliminating the need for travel and reducing wait times for appointments.
Requirements for Third-Party Companies:
To ensure the safe and effective integration of third-party telemedicine applications with hospital EMR and billing systems, third-party companies must fulfill several key requirements:
- Compliance with Data Security Standards: Third-party companies must adhere to strict data security and privacy standards, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations, to protect patient information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Interoperability: Telemedicine platforms should support interoperability standards to facilitate seamless integration with hospital EMRs, ensuring the accurate exchange of patient data and clinical information.
- Scalability and Reliability: Telemedicine solutions should be scalable and reliable to accommodate varying volumes of users and ensure consistent performance during peak usage times.
- Customization and Flexibility: Third-party companies should offer customizable solutions that can be tailored to the specific needs and workflows of healthcare organizations, allowing for seamless integration with existing systems and processes.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Telemedicine platforms must comply with federal and state regulations governing telehealth services, including licensure, prescribing guidelines, and reimbursement policies.
Risks:
Despite the potential benefits, integrating third-party telemedicine applications with hospital EMR and billing systems poses several risks that healthcare organizations should be aware of:
- Data Security Concerns: Integrating external systems with hospital EMRs increases the risk of data breaches or cybersecurity threats, potentially compromising patient confidentiality and data integrity.
- Quality of Care: Inadequate integration or interoperability issues may result in incomplete or inaccurate transmission of patient data, leading to errors in diagnosis, treatment, or medication management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare organizations must ensure that third-party telemedicine platforms comply with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, to avoid legal and financial penalties for non-compliance.
- Patient Engagement and Satisfaction: Poor user experience or technical issues with telemedicine applications may impact patient engagement and satisfaction, leading to dissatisfaction with the quality of care provided.
Federal Regulations:
Several federal regulations govern the integration of third-party telemedicine applications with hospital EMR and billing systems:
- HIPAA: The HIPAA Privacy Rule and Security Rule establish standards for protecting the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI) transmitted or stored by telemedicine platforms and hospital systems.
- HITECH Act: The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act promotes the adoption and meaningful use of electronic health records (EHRs) and sets requirements for the security and privacy of electronic health information.
- Medicare and Medicaid Reimbursement Policies:The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) establish reimbursement policies for telehealth services, including requirements for billing and documentation.
Conclusion:
Integrating third-party telemedicine applications with hospital EMR and billing systems offers significant opportunities to improve care coordination, efficiency, and access to care. However, healthcare organizations must carefully assess the requirements, risks, and regulatory considerations associated with telemedicine integration to ensure patient safety, data security, and regulatory compliance. By partnering with reputable third-party companies and implementing robust security measures, healthcare organizations can leverage telemedicine technology to enhance patient care delivery and outcomes in the digital age.