How Telemedicine Kits are changing Healthcare
To many, the word health kit brings to mind a first aid box that holds gauze, cotton rolls, ointments, and some tablets to treat scrapes and falls. But today health kits are far more advanced and in many industries and scenarios, they are a necessity mandated by law.
These days a health kit is less a first aid box and more of a futuristic diagnostic suitcase filled with devices and strips that would seem more at home on a Star Trek episode. The rise in wireless technology has spread to our medical industry and given birth to a range of portable diagnostic devices and treatment aids.
MEDICAL DEVICES HAVE UNDERGONE A REVOLUTION
Today we find that hospitals and ambulances are equipped with medical monitoring devices that are not just complex in their function but also instantaneous in their working. Gone are the days when we doctors had to use stethoscopes to try and diagnose an arrhythmia or other conditions, today we have a wide range of devices such as single-lead ECG, digital stethoscopes, etc that can monitor the heartbeat and even provide an interpretation of the same to the doctor.
The digital world has been key to the advancement of many fields and medicine or more specifically medical devices are one of them. For most medical students and doctors a manually operated blood pressure machine with mercury in it is an object of the past (many have never seen one in the western countries), there are many devices that our current doctors trained with during their education that are no longer in production or use.
With the advancements in tablets, touch screens, and phones medical devices manufacturers were able to create more compact devices, digital displays, and AI-based programming that can be used for the diagnosis of a variety of illnesses. The rapid progression of programming languages means that medical devices can be created with complex interfacing and diagnostic software. The software can automatically add data to the patient's records, highlight values that are outside expected values, plot readings as charts and graphs, etc.
HOW LICENSING AND REGULATIONS PLAY A ROLE
Medical devices come under a different set of rules and regulations than the ones applied to drugs, and pharmaceuticals in general. They also have different licensing and patenting laws in almost every country, many a time the patent laws, and licensing laws are slanted in favour of the manufacturers of devices. For a new medical device to be patented it has to show the same or better efficacy in diagnosing/evaluating the medical parameter in question as to the previous versions of the device. This meant that while a manually inflated blood pressure cuff that worked with a mercury reservoir was an older generation of medical device, all one had to do is modify it slightly and have a digital display with the same margin of error/accuracy and it was considered a brand new device.
So the medical devices market was less regulated and could still earn a lot from both patients and the medical community by making only incremental changes to a device. This led to the stagnation of medical technology for a while, however, the greatest motivator vis a vis competition in the open market especially from foreign competitors led to rapid growth in the way medical devices were developed. It wasn't just the threat of competition but also the increasing demand from doctors and patients for devices that are faster, more accurate, and smaller in size. Today a smartphone has more computing power than the computers used a decade ago and software, and mobile apps have provided developers with the ability to provide a wide variety of interpretations to a doctor.
The introduction of 3D modelling through computer systems has changed how doctors use CT scans and MRIs, in the same vein we have now moved towards devices that record and transmit data via the internet or Bluetooth.
SMALLER, FASTER, SMARTER
This is the mantra that has gripped the medical devices industry in recent times. The time of wired devices with long, thick, and unwieldy cables is a thing of the past, today hospitals and clinics use devices that can fit into the palm of your hand and take accurate readings in seconds. Today medical devices such as Glucometers that measure blood sugar levels are an indispensable part of life for those suffering from diabetes. During the recent pandemic, we saw how digital thermometers and pulse oximeters became ubiquitous in their use, after all, every mall, bar, and restaurant had one. Monitoring health parameters such as Uric acid or Cholesterol is very important for people suffering from specific diseases such as kidney problems, heart attacks, etc.
The ageing population in the world is ever-increasing, and advances in medical care have drastically increased the average life expectancy. This means that over the years the focus has shifted from illness care to wellness care. This means that medical devices are increasingly finding their way from the hospitals to our homes. All of this boils down to the simplicity of design, the versatility of the device, and the portability of the device.
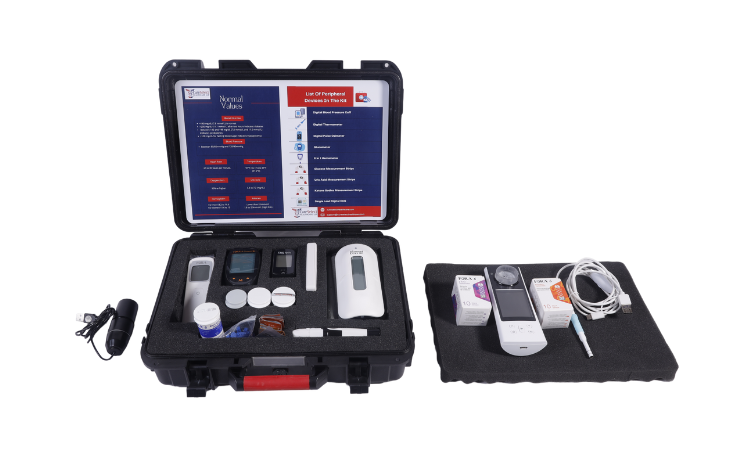
REMOTE MONITORING KITS
These kits are a collection of medical devices that are usually Bluetooth enabled, and WiFi-enabled, so they can be used to record and monitor a variety of medical data about you in real-time and transmit the data to your doctor. These kits are designed in such a way as to cover the most important and most commonly monitored medical parameters. These include your blood sugar, blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, pulse rate, cholesterol, uric acid, haemoglobin, and WBC counts. There are specific kits that are extremely useful for people with specific illnesses such as heart attacks, like the cardiac troponin kit, etc.
These telemedicine kits can help people with chronic and long-term illnesses to keep a check on their health without having to make arduous visits to the hospital or subject themselves to expensive tests at labs, this can cut down response time, help older people keep a strict and regular watch on their health, etc. in many countries home healthcare and geriatric care have gained a huge amount of traction, there are many hospitals and clinics that offer at-home consultations for people, they use a variety of instruments that can take readings at the bedside which they then evaluate and communicate to the doctor, or port them to their respective hospitals or doctors via the internet.
Any and all devices used for such a purpose come under the umbrella of remote health monitoring devices and an assembly of any combination of them is called a kit. In the increasingly complex medical world, there are kits that have been assembled for specific purposes with devices tailor-made to detect and treat the condition. Some examples of this include cardiac monitoring kits, which contain cardiac troponin c tests, handheld ECG, etc among other things that help patients who have had cardiac episodes or are at risk of one.
HOW DOES TELEMEDICINE TIE IN
In all of the cases we talked about above, one critical thing is missing, and that is intervention or treatment by a qualified medical doctor. The best way to combine remote health monitoring with early intervention and care is via Telehealth or Telemedicine services being tacked on as well. The COVID pandemic proved how invaluable telemedicine can be for doctors in an overworked and overcrowded healthcare system. But doctors need to be armed with data, more specifically they need real-time data on various health parameters of the patient in order to make an informed diagnosis, or to prescribe medications. Kits that are equipped with Wifi or Bluetooth-enabled devices can bridge this gap by providing data in real-time.
Here's the best part, most often you don't need to be a trained professional to use these devices to take the readings, this means that friends, family, coworkers, health aids, nursing home staff, etc can use these devices without extensive training. They can then either send the results to a remote doctor who then decides what to do, or they can simply read out the values during the teleconsult. Thus saving time, allowing early intervention and saving lives.
The use of telemedicine works best in tandem with devices, monitors and a decent internet connection, many countries have brought telemedicine into the fold of mainstream healthcare with specific rules, codes, insurance payout structures etc. Thus it only makes sense to make full use of the service and gain maximum benefits from it.
TO CONCLUDE
Remote patient monitoring is not a new concept but the advent of new technology, increase in connectivity and the rapid rise in the smartphone/tablet industry have ensured that there is infinitely greater connectivity and multiple options for connectivity available to individuals, this has made them undergo an evolution. For telemedicine to live up to its full scope it needs to be paired with a lot of data and it is in such situations that remote health monitoring kits, or telemedicine kits as they can be rightly called, come into play.